👨🏫 Notes
Bond Pricing Review
General (Coupon):
Zero Coupon:
Consol:
F is Face Value, c is the coupon rate, i is the YTM or the interest rate on comparable bonds, etc.
To calculate bond price or yield on a coupon bond or a zero coupon bond, just use a spreadsheet or a calculator. For a consol, you will need to use the formula.
✏️ A consol pays $10,000 every year. Its yield to maturity is 5%. What is its price?
✔ Click here to view answer
✏️ A consol that pays $10,000 every year costs $180,000. What is its yield to maturity?
✔ Click here to view answer
Yield to Maturity (YTM): Interest rate that makes the present value of the bond’s payments equal to its price.
- To find it, solve one of the above bond pricing formulas for i.
- Pay attention to how returns are presented with bonds.
Yield to maturity = 3% per half year (periodic rate r(T))
Bond Equivalent Yield = 3%*2 = 6% (assumes no reinvestment of coupons/simple interest/it’s an APR)
Effective Annual Rate = (1+3%)2-1 = 6.09% (assumes reinvestment/compound interest)

Duration
Duration of a perpetuity is (1+y)/y
Duration of a Zero Coupon Bond is T
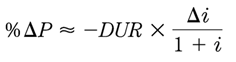
See the following page for how to calculate duration quickly in a spreadsheet: 🔎 Quick duration calculations
What Determines Duration?
Rule 1: The duration of a zero-coupon bond equals its time to maturity
Rule 2: Holding maturity constant, a bond’s duration is higher when the coupon rate is lower
Rule 3: Holding the coupon rate constant, a bond’s duration generally increases with its time to maturity
Rule 4: Holding other factors constant, the duration of a coupon bond is higher when the bond’s yield to maturity is lower
Rules 5: The duration of a level perpetuity is (1 + y) / y